As a professional in your field, it’s important to make sure that all equipment used in your work is up to safety and functionality standards. To ensure this, regular equipment inspections are necessary. A comprehensive equipment checklist is an effective tool for conducting these inspections. Here is a sample equipment checklist that you can use to guide your own inspections.
Equipment Checklist
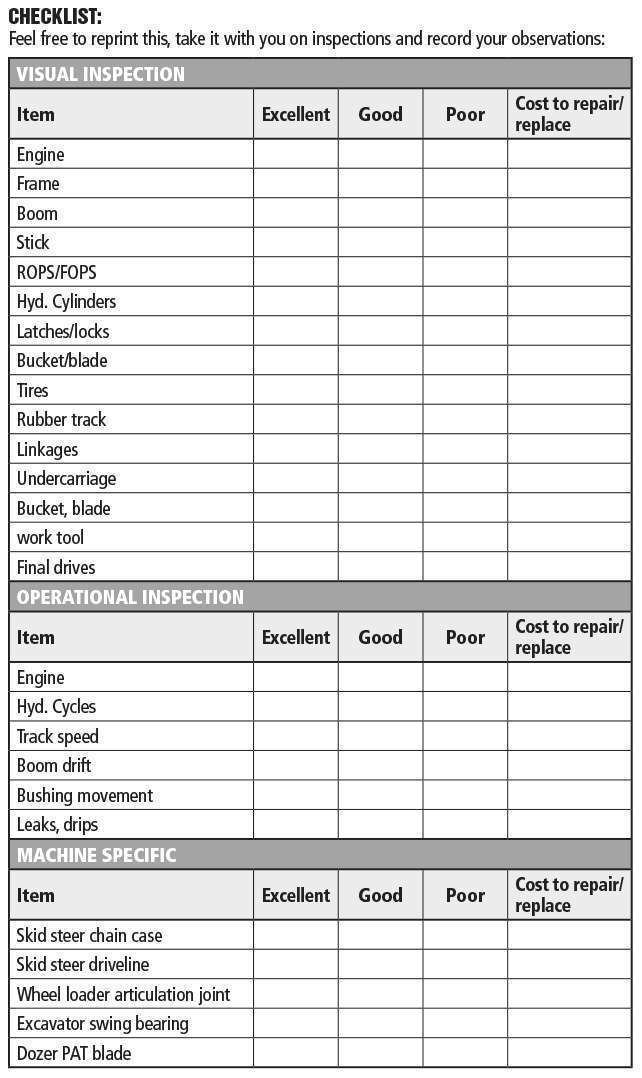 When conducting equipment inspections, it’s best to work through each item on the checklist systematically. This will help you to keep track of what you’ve checked and what still needs to be inspected. Here are the items that should be included in your equipment checklist:
When conducting equipment inspections, it’s best to work through each item on the checklist systematically. This will help you to keep track of what you’ve checked and what still needs to be inspected. Here are the items that should be included in your equipment checklist:
- General safety check
- Main power supply check
- Grounding check
- Equipment stability check
- Accessory equipment check
- Functional check
- Visual and precision inspection
- Cleaning and maintenance
1. General Safety Check
The general safety check ensures that all the necessary safety precautions are observed when using the equipment. It covers the following areas:
- Emergency stop controls
- Emergency stop switch
- Warning labels
- Guarding devices
- Electrical safety
2. Main Power Supply Check
The main power supply check ensures that the equipment is connected to the correct power source and voltage. It also ensures that the power supply is functioning properly. The key things to check are:
- Power cord
- Connection to power outlet
- Power source voltage
- Circuit breaker or fuse
- Battery condition, if applicable
3. Grounding Check
The grounding check ensures that the equipment is properly grounded, which is a vital safety measure. This should be done in accordance with the equipment manufacturer’s instructions and standard safety guidelines. The key areas to check are:
- Ground wire condition
- Ground continuity
- Ground prong contact
- Grounding resistance
4. Equipment Stability Check
The equipment stability check ensures that the equipment is stable and secure during use. Unstable or wobbly equipment is a safety hazard and can cause damage or injury. The key areas to check are:
- Equipment level
- Equipment placement
- Surface condition
- Fastenings and fixings
- Stabilizing devices
5. Accessory Equipment Check
The accessory equipment check ensures that all accessories that are used with the equipment are in good condition and functioning properly. This includes items such as hoses, fittings, adapters, and regulators. The key areas to check are:
- Accessory equipment condition
- Accessory equipment compatibility
- Accessory equipment fit and alignment
- Accessory equipment sealing and connections
6. Functional Check
The functional check ensures that the equipment is working as intended and that there are no malfunctions or defects. This is done through a series of tests and measurements. The key areas to check are:
- Operation of controls
- Operation of moving parts
- Performance of equipment functions
- Output measurement and recording
- Noise and vibration levels
7. Visual and Precision Inspection
The visual and precision inspection ensures that there are no signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or damage to the equipment. This is done through close inspection of the equipment’s components and surfaces. The key areas to check are:
- Surface finish and coating
- Wear and tear on moving parts
- Corrosion or rust on surfaces
- Cracks or damage to components
8. Cleaning and Maintenance
The cleaning and maintenance check ensures that the equipment is clean and well-maintained. This is essential for longevity and reliability of the equipment, as well as ensuring that it remains safe to use. The key areas to check are:
- Cleanliness of equipment surfaces
- Cleaning of filters and screens
- Lubrication of moving parts
- Replacement of worn parts
- Storing the equipment properly
Conclusion
By conducting regular equipment inspections using a thorough equipment checklist such as the one outlined above, you can ensure that your equipment is always safe and functioning properly. This can help you to avoid damage to the equipment, prevent injuries, and save valuable time and resources. Remember to consult the equipment manufacturer’s instructions and relevant safety guidelines when conducting inspections, and to always wear appropriate personal protective equipment.