High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can lead to serious health complications if left untreated, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. That’s why it’s important to monitor your blood pressure regularly and keep track of the readings.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. It’s measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). The systolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart beats, while the diastolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart rests between beats.
Why Should You Monitor Your Blood Pressure?
Monitoring your blood pressure is important for several reasons:
- It helps you detect high blood pressure early, before it causes any symptoms.
- It enables you and your healthcare provider to track your blood pressure over time and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary.
- It helps you monitor the effectiveness of your medications and lifestyle changes.
- It empowers you to take control of your health and make informed decisions about your care.
How to Monitor Your Blood Pressure
There are two ways to monitor your blood pressure:
1. At Home
You can monitor your blood pressure at home using a blood pressure monitor. These devices are available over-the-counter and are easy to use. Just wrap the cuff around your upper arm, press a button, and wait for the reading. Make sure you follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use.
When you measure your blood pressure at home:
- Take your readings at the same time every day, preferably in the morning before taking any medications.
- Sit quietly for at least five minutes before taking your readings.
- Rest your arm on a table or armrest with your palm facing up and the cuff at heart level.
- Take at least two readings, one minute apart, and record them both.
2. At Your Healthcare Provider’s Office
Your healthcare provider can also monitor your blood pressure during routine check-ups. They will use a blood pressure cuff and a stethoscope to measure your blood pressure manually. This method is more accurate than using a blood pressure monitor at home, but it’s less convenient.
When you measure your blood pressure at your healthcare provider’s office:
- Wear comfortable clothing that can be easily rolled up above your elbow.
- Sit quietly for at least five minutes before taking your readings.
- Rest your arm on a table or armrest with your palm facing up and the cuff at heart level.
- Take at least two readings, one minute apart, and record them both.
How to Use a Blood Pressure Log
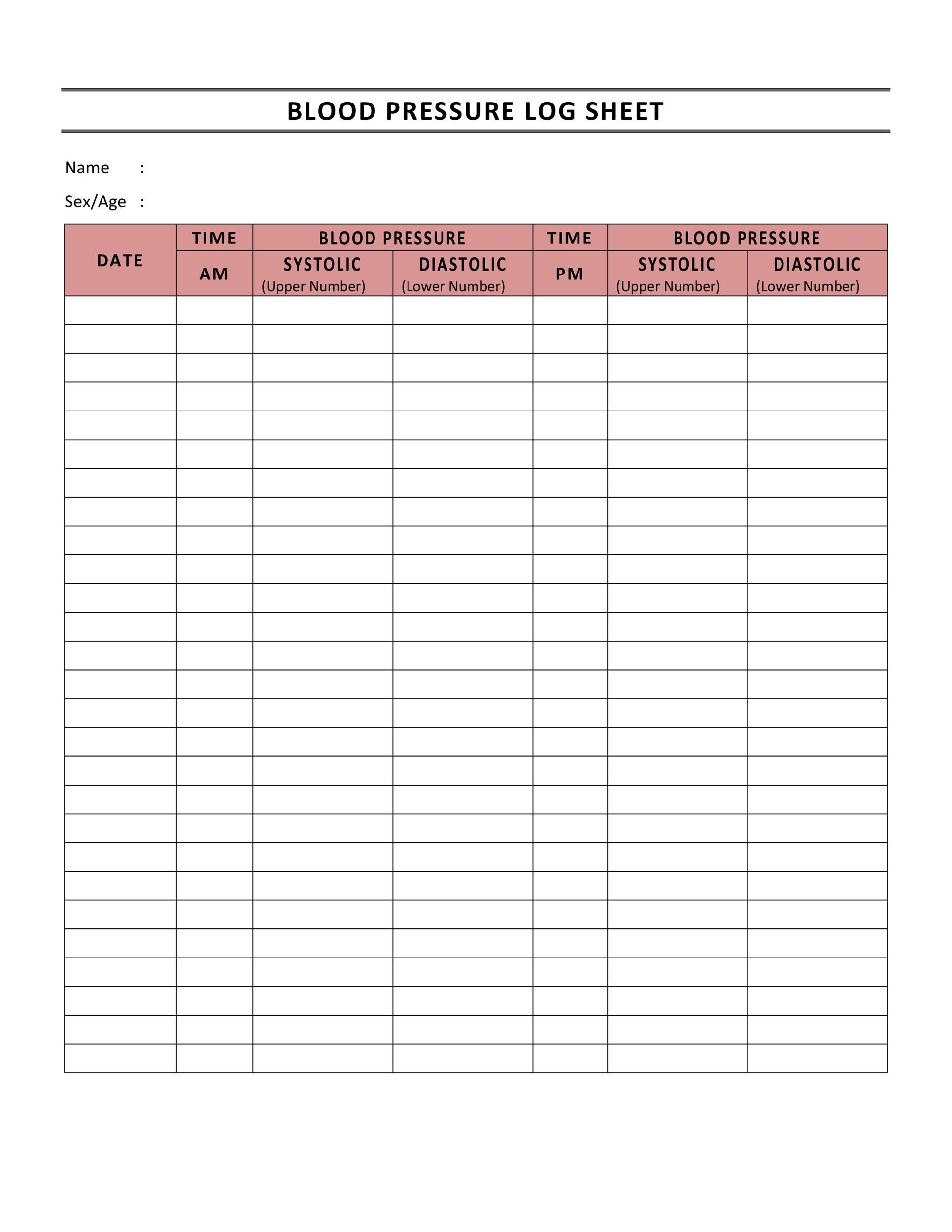
A blood pressure log is a tool you can use to keep track of your blood pressure readings over time. It’s a simple document that allows you to record each reading, along with the date and time it was taken. By tracking your readings, you and your healthcare provider can detect trends and make informed decisions about your care.
1. Choose a Blood Pressure Log Template
There are many blood pressure log templates available online that you can use for free. Choose one that suits your needs and download it to your computer.
2. Print the Template
Once you’ve downloaded the template, print out several copies so you have enough for at least a month’s worth of readings.
3. Record Your Readings
When you take your blood pressure, record the reading on the log along with the date and time it was taken. You can also record any notes about your health at the time of the reading, such as any medications you took or how you were feeling.
4. Bring Your Log to Your Healthcare Provider
At your next healthcare provider visit, bring your blood pressure log with you. Your healthcare provider can review your readings and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
Monitoring your blood pressure is an important part of maintaining good health. By tracking your readings and using a blood pressure log, you can work with your healthcare provider to manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications.